Retrieval
Many LLM applications require user-specific data that is not part of the model's training set. The primary way of accomplishing this is through Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG). In this process, external data is retrieved and then passed to the LLM when doing the generation step.
LangChain provides all the building blocks for RAG applications - from simple to complex. This section of the documentation covers everything related to the retrieval step - e.g. the fetching of the data. Although this sounds simple, it can be subtly complex. This encompasses several key modules.
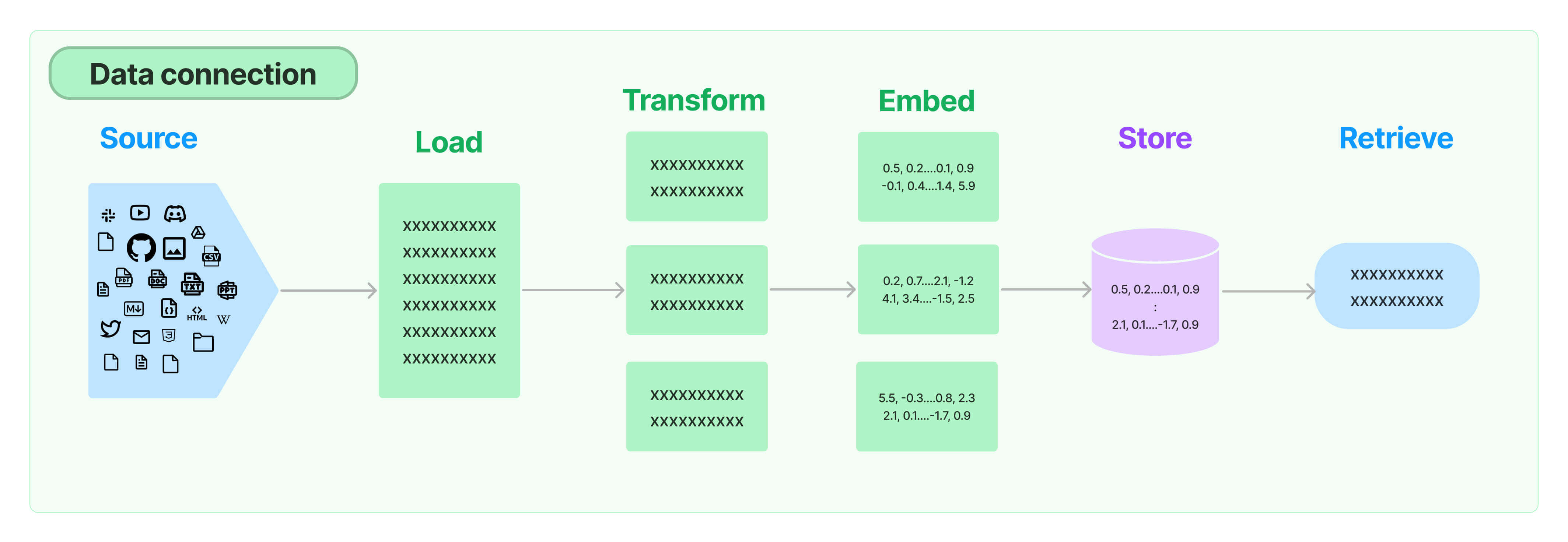
Document loaders load documents from many different sources. LangChain provides over 100 different document loaders as well as integrations with other major providers in the space, like AirByte and Unstructured. LangChain provides integrations to load all types of documents (HTML, PDF, code) from all types of locations (private S3 buckets, public websites).
A key part of retrieval is fetching only the relevant parts of documents. This involves several transformation steps to prepare the documents for retrieval. One of the primary ones here is splitting (or chunking) a large document into smaller chunks. LangChain provides several transformation algorithms for doing this, as well as logic optimized for specific document types (code, markdown, etc).
Another key part of retrieval is creating embeddings for documents. Embeddings capture the semantic meaning of the text, allowing you to quickly and efficiently find other pieces of a text that are similar. LangChain provides integrations with over 25 different embedding providers and methods, from open-source to proprietary API, allowing you to choose the one best suited for your needs. LangChain provides a standard interface, allowing you to easily swap between models.
With the rise of embeddings, there has emerged a need for databases to support efficient storage and searching of these embeddings. LangChain provides integrations with over 50 different vectorstores, from open-source local ones to cloud-hosted proprietary ones, allowing you to choose the one best suited for your needs. LangChain exposes a standard interface, allowing you to easily swap between vector stores.
Once the data is in the database, you still need to retrieve it. LangChain supports many different retrieval algorithms and is one of the places where we add the most value. LangChain supports basic methods that are easy to get started - namely simple semantic search. However, we have also added a collection of algorithms on top of this to increase performance. These include:
- Parent Document Retriever: This allows you to create multiple embeddings per parent document, allowing you to look up smaller chunks but return larger context.
- Self Query Retriever: User questions often contain a reference to something that isn't just semantic but rather expresses some logic that can best be represented as a metadata filter. Self-query allows you to parse out the semantic part of a query from other metadata filters present in the query.
- Ensemble Retriever: Sometimes you may want to retrieve documents from multiple different sources, or using multiple different algorithms. The ensemble retriever allows you to easily do this.
- And more!
The LangChain Indexing API syncs your data from any source into a vector store, helping you:
- Avoid writing duplicated content into the vector store
- Avoid re-writing unchanged content
- Avoid re-computing embeddings over unchanged content
All of which should save you time and money, as well as improve your vector search results.